2020 Supplier Overview Part 2- Cloud
The January 28th Telarus Tuesday call welcomed CPO & co-founder, Patrick Oborn and VP of biz dev – Cloud, Koby Phillips to discuss Cloud selling strategies and how Telarus’ robust portfolio of solution providers can solve your customer’s most challenging IT problems.
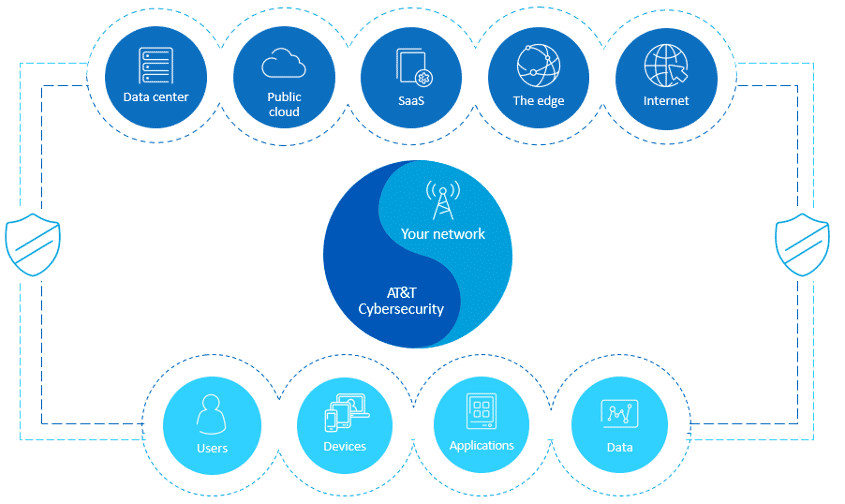
Different Types of Clouds
Everyone is using the Cloud – how and how much is the question. Cloud itself can be complex, but Telarus is here to help and has the team and supplies to support your opportunities. So, what are the different types of Clouds?
- Private Cloud – This is when the Cloud environment is dedicated to only one user or sometimes a group of related users. Private Cloud is typically in a third-party data center or on-prem.
- Public Cloud – In a public Cloud, there are shared servers and other services between multiple users. Public Cloud computing uses Cloud computing technologies to support customers that are external to the provider’s organization.
Whenever you want to connect multiple Clouds or traditional infrastructure into some Clouds, this creates a Hybrid Cloud environment.
Speaking the Language: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS
The different layers of the infrastructure pyramid include IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
- IaaS (Infrastructure and Network Architecture) – In the IaaS model, third-party service providers host various IT components for customers in a highly automated delivery model that can be either a single or multi-tenant environment. In some cases, IaaS providers extend into tasks such a systems maintenance, data backup, and business continuity offerings.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) – PaaS offerings include application design, development, testing, and deployment. PaaS services can also include web service integration, development team collaboration, database integration, and information security.
- SaaS (Software as a Service) – SaaS is a software distribution model in which a service provider hosts applications for customers and makes them available to these customers via the internet. As with other Cloud services, organizations typically pay for SaaS applications through a subscription fee on a monthly or annual basis. A lot of end-users prefer this over the traditional model of paying for software through a perpetual license.
 There has been an evolution when it comes to Mission Critical Computing; this has happened to keep up with the demand to have access to the most recent technology. Many businesses have had to shift to the Cloud to scale and deploy in a more cost- and time-effective way than what legacy architecture allowed.
There has been an evolution when it comes to Mission Critical Computing; this has happened to keep up with the demand to have access to the most recent technology. Many businesses have had to shift to the Cloud to scale and deploy in a more cost- and time-effective way than what legacy architecture allowed.
 Colocation 101
Colocation 101
There are various considerations when a customer is trying to locate a data center that makes sense for their private Cloud and their own private infrastructure needs.
- Geographic Considerations
- Physical Security Considerations
- Connectivity Considerations
- Power Consumption Considerations
- Sustainable Energy Considerations
- Temperature Considerations
- Cross-Connect Considerations
- Future Expansion Considerations
Telarus has an immense amount of data center providers available to partners and their end-users. Take a look below to see what colocation providers you can find in the Telarus portfolio:
 Cloud Connectivity 101
Cloud Connectivity 101
When it comes to direct Cloud connectivity, the diagram below can highlight the ability to access multiple Cloud Service Providers from a single port. This is generally done via the Equinix Cloud Exchange Fabric, Coresite’s Interconnect Gateway, or a supplier like Megaport, amongst others.
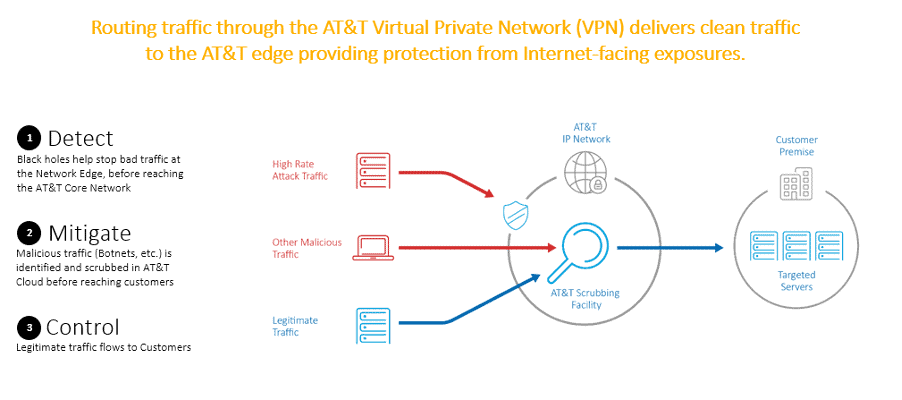 There more than a few different suppliers that offer direct Cloud connectivity. Many of the suppliers in the Telarus portfolio have CSP On-Ramps in their facilities. A Cloud “On-Ramp” is a connection service inside a data center that provides direct connectivity to a specific Cloud provider. This is generally where a Cloud has gone. Others can resell the connection in the managed offering or connect to the on-ramps from the customer’s location.
There more than a few different suppliers that offer direct Cloud connectivity. Many of the suppliers in the Telarus portfolio have CSP On-Ramps in their facilities. A Cloud “On-Ramp” is a connection service inside a data center that provides direct connectivity to a specific Cloud provider. This is generally where a Cloud has gone. Others can resell the connection in the managed offering or connect to the on-ramps from the customer’s location.
 Below you can see what Private Cloud Providers and Cloud Application Providers work with Telarus as well:
Below you can see what Private Cloud Providers and Cloud Application Providers work with Telarus as well:

 Telarus also works with multiple suppliers who can help access, migrate, and manage a customer’s data and applications into the Cloud.
Telarus also works with multiple suppliers who can help access, migrate, and manage a customer’s data and applications into the Cloud.
 IaaS vs. Bare Metal
IaaS vs. Bare Metal
Some may ask what the difference between Bare Metal as a Service and IaaS. With both, you gain access to a server on which you can install and run your chosen OS and applications. However, with bare metal, you get control of the full stack, from the tin right up to the user interface. You can also optimize utilization and performance to a granular level, something you cannot do in a virtualized environment. Like every technology, each has its place in the world, depending on the needs of the customer. Below you can see a list of IaaS and Bare Metal suppliers who work with Telarus.
 DaaS & VDI
DaaS & VDI
DaaS, which is a fully managed VDI hosted in the Cloud, is one of the most common Cloud services. This is mostly due to the emergence of remote workers. There are many additional benefits to DaaS that align with the overall benefits to the Cloud.
 Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery
Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery
When it comes to Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery, a couple of key selling points include the ability to provide rapid recovery, geographic separation from the originating source, and flexibility.
 Managed IT as a Service
Managed IT as a Service
Managed IT allows for full management of all or certain aspects of an organization’s IT needs. Some companies outsource a portion of duties to a managed IT offering to enable their staff to focus on other projects, while other companies outsource all their IT needs.
 Cloud is complex, but it’s important to remember that everyone is using Cloud, and at the end of the day, it is all about the end-user experience and how the Cloud can benefit your customers.
Cloud is complex, but it’s important to remember that everyone is using Cloud, and at the end of the day, it is all about the end-user experience and how the Cloud can benefit your customers.
To learn more about Telarus, visit www.telarus.com.
